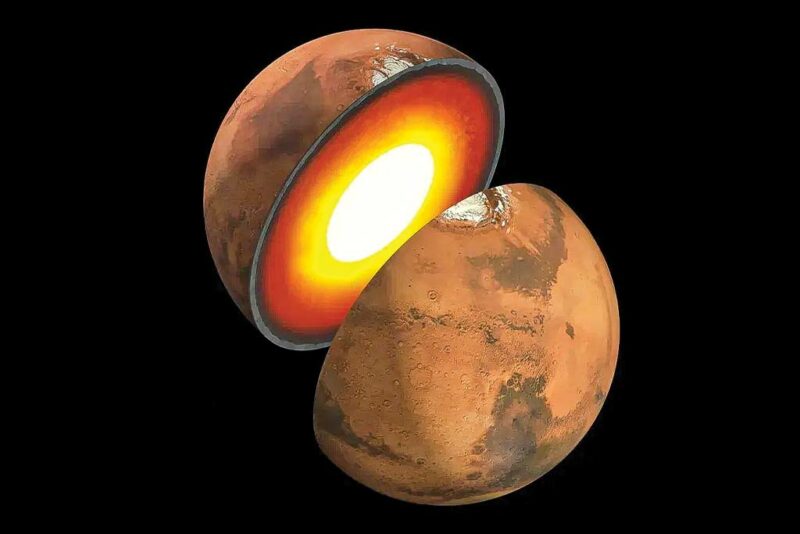

Based on data gathered by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Insight rover, it was found that a layer of molten rock that was previously unknown to scientists surrounds the Martian core.

Based on data gathered by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s (NASA) Insight rover, it was found that a layer of molten rock that was previously unknown to scientists surrounds the Martian core. The silicate layer is approximately 150kms thick and covers Mars’ liquid metallic core. Scientists reassessed Mars’ interior with the help of information from Insight’s seismometer following a meteorite impact that occurred in 2021. Studying the seismic waves produced by the impact led scientists to discover the previously unknown molten layer and gave them insights into Mars’ structure. On reassessing the Red Planet’s core, it was found that it is smaller in size and has a volume that is lesser than what was estimated previously.
Did You Know?
The highest mountain in the solar system, Olympus Mons, is located on Mars. It is approximately 78,740ft high.





